Most Missed Family Medicine Exam Question - Meningitis vs Endocarditis
Most Missed Family Medicine Question — Meningitis vs Endocarditis. Quick answer, key CSF and exam clues for Family Medicine board prep.
ARDS ventilation mortality benefit: low tidal volume ~6 mL/kg predicted/ideal body weight and plateau pressure ≤30. EM board-style question review.
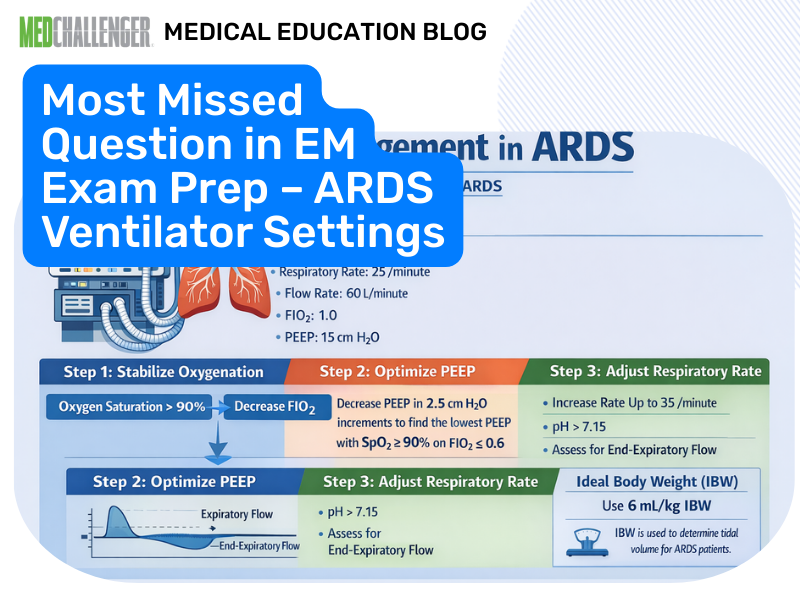
ARDS board questions reliably reward recognition of low tidal volume ventilation (~6 mL/kg predicted/ideal body weight) with plateau pressure limitation as the intervention linked to improved mortality.
You intubate a 30-year-old woman for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Which of the following respirator settings is associated with decreased mortality in patients with ARDS?
Answer Options:
A. Plateau pressure > 30 cm H2O
B. Positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) of 10-15 H2O
C. Peak inspiratory pressure > 30 cm H2O
D. Tidal volume 6 to 7 mL/kg/ideal body weight (IBW)
Low tidal volume ventilation (classically 6 mL/kg predicted/ideal body weight) is the most consistently guideline-backed ventilator strategy associated with improved mortality in ARDS, along with limiting plateau pressure to ≤30 cm H₂O (ATS/ESICM/SCCM 2017). PEEP is generally used in ARDS and titrated to oxygenation and recruitability (often via PEEP/FiO₂ tables); it is not accurate to teach “little or no PEEP” as a mortality-improving strategy.
| Option | What It Tests / Implies | Why It’s Wrong Here |
|---|---|---|
| A. Plateau pressure > 30 cm H₂O | Understanding of plateau pressure limits | Plateau pressures **>30** increase risk of ventilator-induced lung injury; guidelines emphasize **≤30 cm H₂O**. |
| B. PEEP 10–15 cm H₂O | PEEP selection in ARDS | PEEP is not a single fixed mortality setting; ARDS management uses **PEEP/FiO₂ titration** (and often higher PEEP in more severe ARDS), not “10–15” as a universal mortality-improving choice. |
| C. Peak inspiratory pressure > 30 cm H₂O | Confusion between peak vs plateau pressure | Peak pressure reflects airway resistance + compliance; targeting a *high* peak pressure is not protective and is not the mortality-linked parameter. |
| D. Tidal volume 6–7 mL/kg IBW | Lung-protective low VT ventilation | This is the best-supported mortality-reducing setting (conceptually **~6 mL/kg PBW/IBW**, within 4–8) in ARDS. |
In ARDS, the mortality-associated ventilator strategy is low tidal volume (~6 mL/kg PBW/IBW) while keeping plateau pressure ≤30 cm H₂O.
1. Identify the ventilator parameter in ARDS with the strongest association with reduced mortality: low tidal volume based on predicted/ideal body weight.
2. Distinguish plateau pressure (alveolar distending pressure; target ≤30) from peak inspiratory pressure (includes airway resistance) in ARDS test questions.
This item exploits two common board traps: (1) offering “high pressure” options that sound like they might improve ventilation but actually worsen VILI risk, and (2) offering a plausible PEEP range even though PEEP is titrated and not the single most test-reliable mortality association compared with low VT based on PBW/IBW.
A 68-year-old man meets Berlin criteria for ARDS. Which initial tidal volume is most appropriate to reduce ventilator-induced lung injury?
- A. 10–12 mL/kg actual body weight
- B. 6 mL/kg predicted (ideal) body weight
- C. 8–10 mL/kg ideal body weight
- D. 4 mL/kg actual body weight for all patients
- E. 12–15 mL/kg ideal body weight
A — Review: Too high; increases volutrauma risk.
B — Correct response!: Low VT (~6 mL/kg PBW) is guideline-supported lung-protective ventilation (ATS/ESICM/SCCM 2017).
C — Review: Upper range can be acceptable in some contexts, but the classic mortality-linked target is ~6 mL/kg PBW.
D — Review: 4 mL/kg may be used selectively but is not a universal starting point.
E — Review: Historical/high VT strategy; harmful in ARDS.
Which ventilator change has the best evidence for mortality reduction in ARDS?
- A. Increase tidal volume to normalize PaCO₂
- B. Avoid permissive hypercapnia at all costs
- C. Reduce tidal volume to ~6 mL/kg predicted body weight
- D. Use zero PEEP to prevent barotrauma
- E. Increase FiO₂ to 1.0 indefinitely
A — Review: Normalizing CO₂ with higher VT worsens VILI.
B — Review: Permissive hypercapnia may be acceptable when adhering to lung-protective ventilation.
C — Correct response!: Low VT lung-protective ventilation is the most exam-reliable mortality benefit.
D — Review: “Zero PEEP” is not recommended in ARDS; PEEP is used to prevent cyclic alveolar collapse.
E — Review: Prolonged maximal FiO₂ risks oxygen toxicity; use PEEP/FiO₂ titration.
A 5'2" (157 cm) woman with obesity is ventilated for ARDS. To set lung-protective ventilation, tidal volume should be calculated using:
- A. Actual body weight
- B. Predicted/ideal body weight based on height and sex
- C. BMI category
- D. Lean body mass measured by bioimpedance
- E. Body surface area
A — Review: Overestimates VT in obesity and increases VILI risk.
B — Correct response!: ARDS VT targets are based on PBW/IBW (height/sex), not actual weight.
C — Review: BMI doesn’t directly determine lung size.
D — Review: Not standard for ventilator VT calculation.
E — Review: Not used for setting ARDS VT.
How would your ventilator adjustments differ between (1) ARDS with severe hypoxemia requiring escalating PEEP/FiO₂ and (2) obstructive physiology with high peak pressures but normal plateau pressures?
Find this and other Emergency Medicine exam prep questions in Med-Challenger Emergency Medicine Review with CME
Try for free and save. Ace your exams and meet your CME/MOC requirements for just $35 a month!
No matter your program, no matter the size, Med-Challenger for Groups and Institutions can better prepare your program or group, fulfill industry requirements, and increase test scores.
Most Missed Family Medicine Question — Meningitis vs Endocarditis. Quick answer, key CSF and exam clues for Family Medicine board prep.
Learn how to prepare for EM boards. emergency medicine board exam study guide. Pass the ABEM board exam, guaranteed. ABEM exam tips.
How to prepare for your family medicine board exam. ABFM study guide. How to pass the ABFM board exam. ABFM exam tips.
Stay informed of new medical education content, certification requirements and deadlines, case-based CME quizzes, and special offers.